1.6: Monopoly II: Consequences
ECON 326 · Industrial Organization · Spring 2020
Ryan Safner
Assistant Professor of Economics
safner@hood.edu
ryansafner/IOs20
IOs20.classes.ryansafner.com
Social Consequences of Monopoly
Perfectly Competitive Market: Takeways
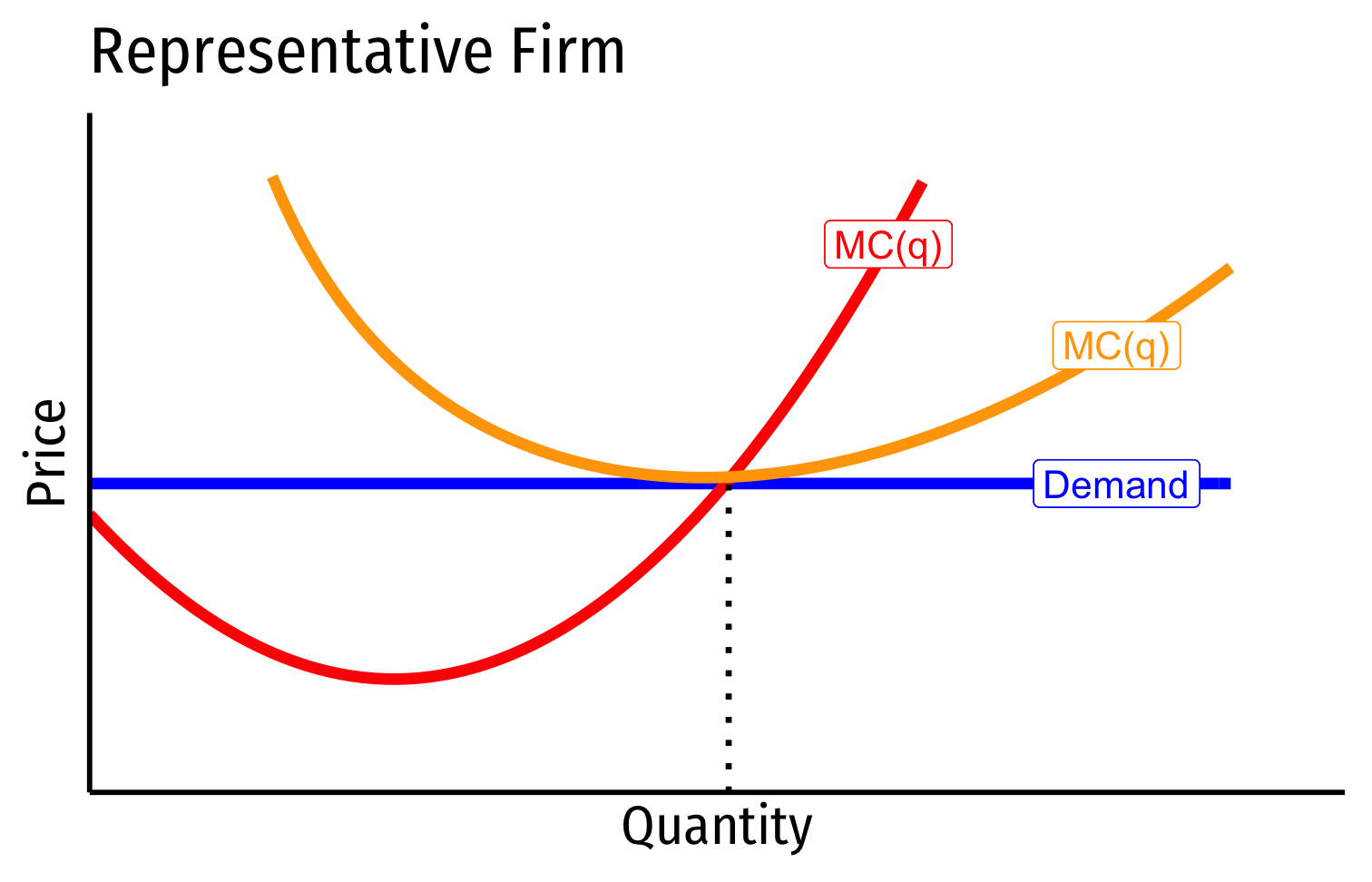
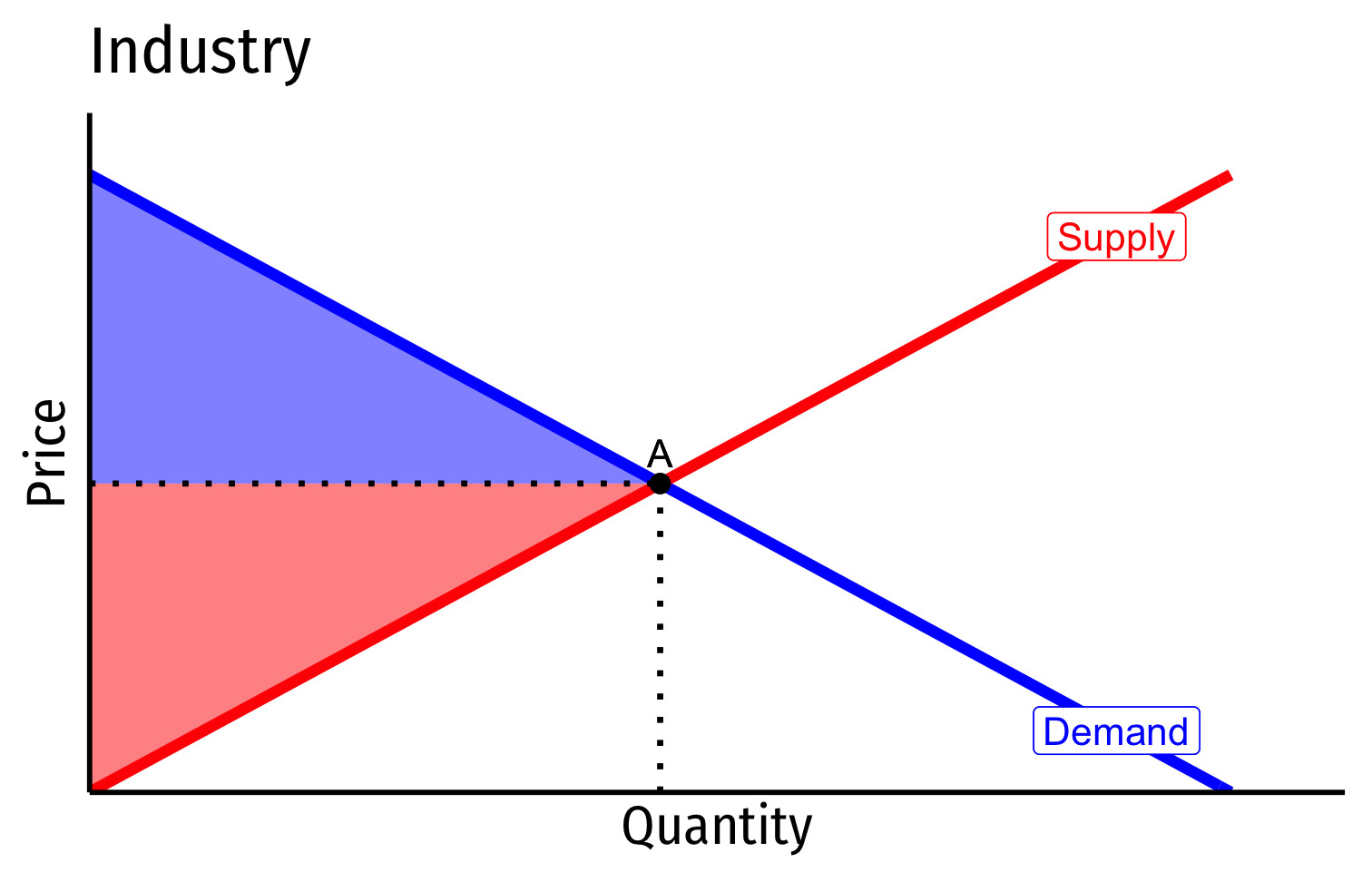
- In a competitive market in long run equilibrium:
- Economic profit is driven to $0
- Allocatively efficient: p=MC(q), maximized CS + PS
- Productively efficient: p=AC(q)min (otherwise firms would enter/exit)
The Bad of Monopoly: DWL I
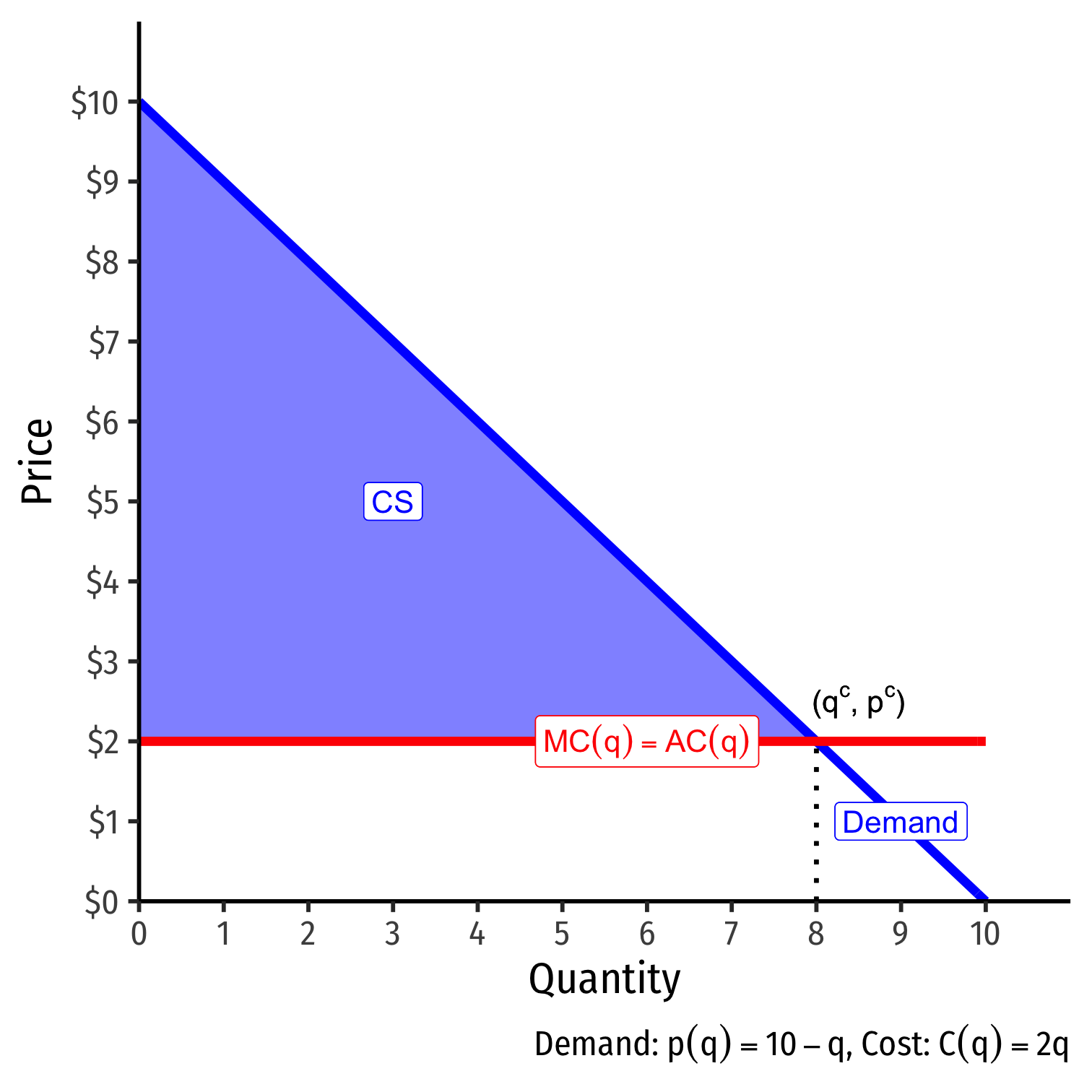
Consider a market with some simplified cost assumptions:
- No fixed costs
- Constant variable costs 2q
- implies MC(q)=AC(q)=2
If this was a competitive market, firms would set p=MC(q) and produce 8
- Consumer surplus maximized
The Bad of Monopoly: DWL II
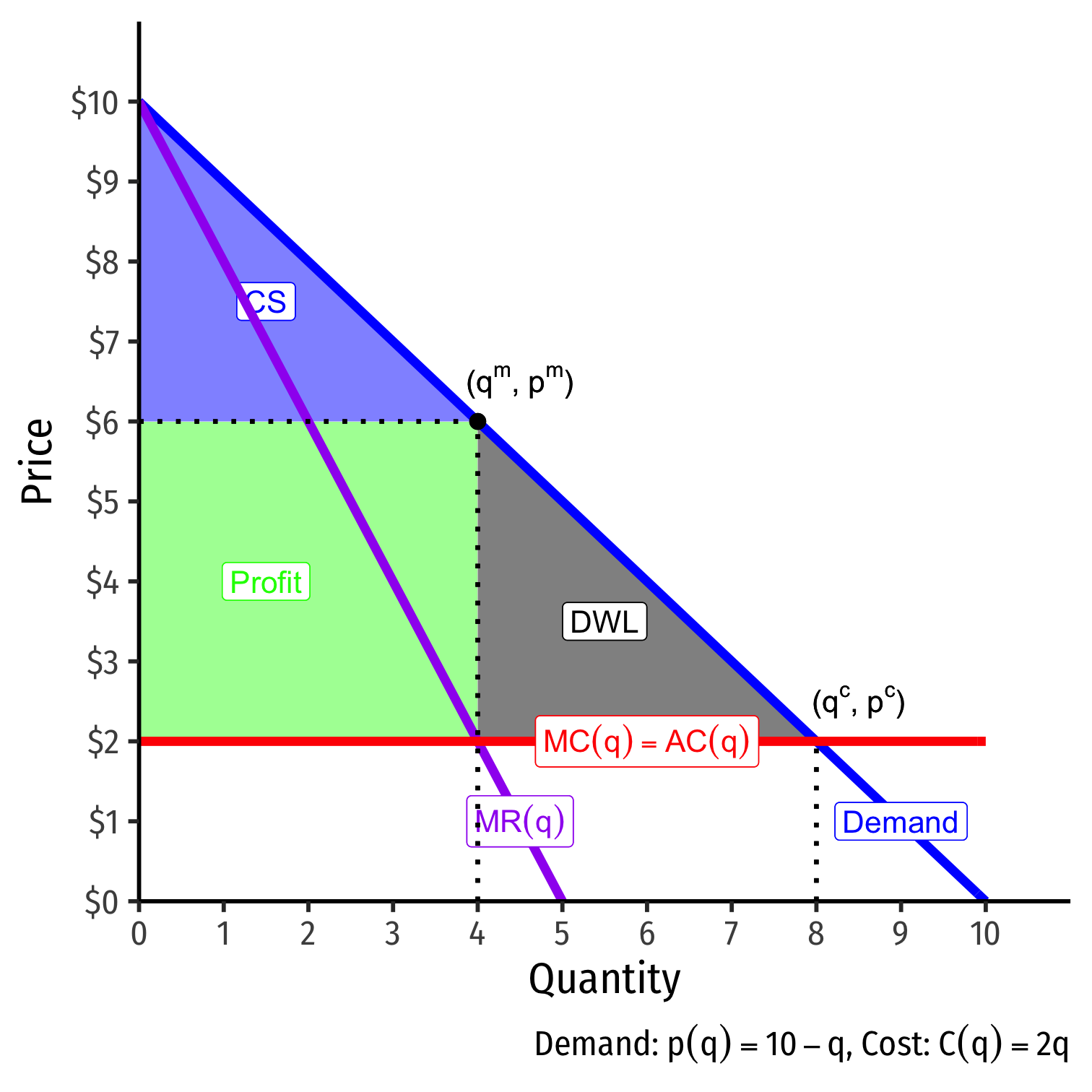
A monopolist faces the entire market demand and sets (qm,pm):
- Sets MR(q) = MC(q) at 4
- Raises price to maximum consumers are WTP (Demand): $6
Restricts output and raises price, compared to competitive market
Earns monopoly profits (p>AC)
Loss of consumer surplus
The Bad of Monopoly II
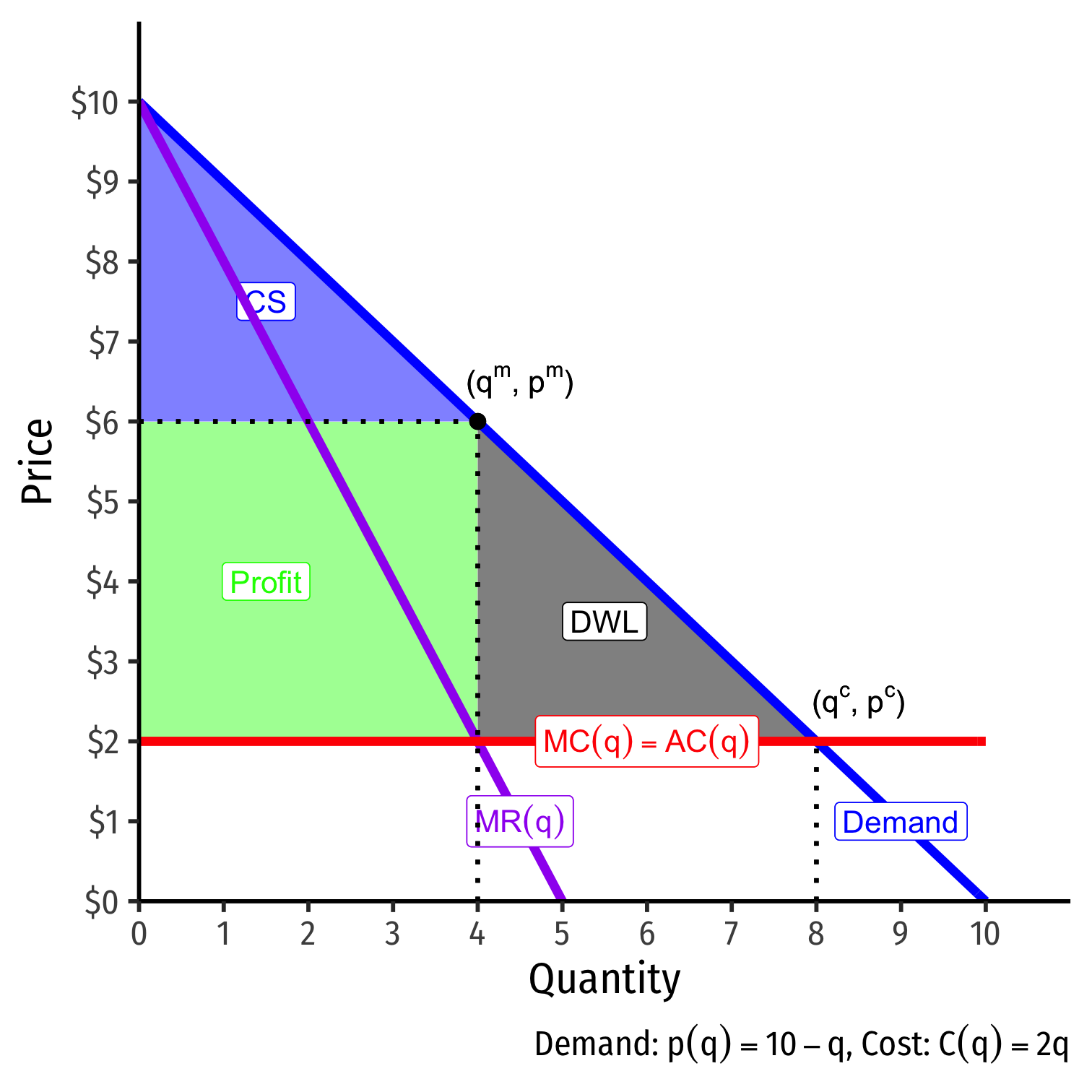
- Deadweight loss of surplus destroyed from lost gains from trade
- Consumers willing to buy more than 4 units for lower prices!
- Monopolist willing to accept lower prices to sell more, but would earn less total profits this way
The Bad of Monopoly: X-Inefficiency
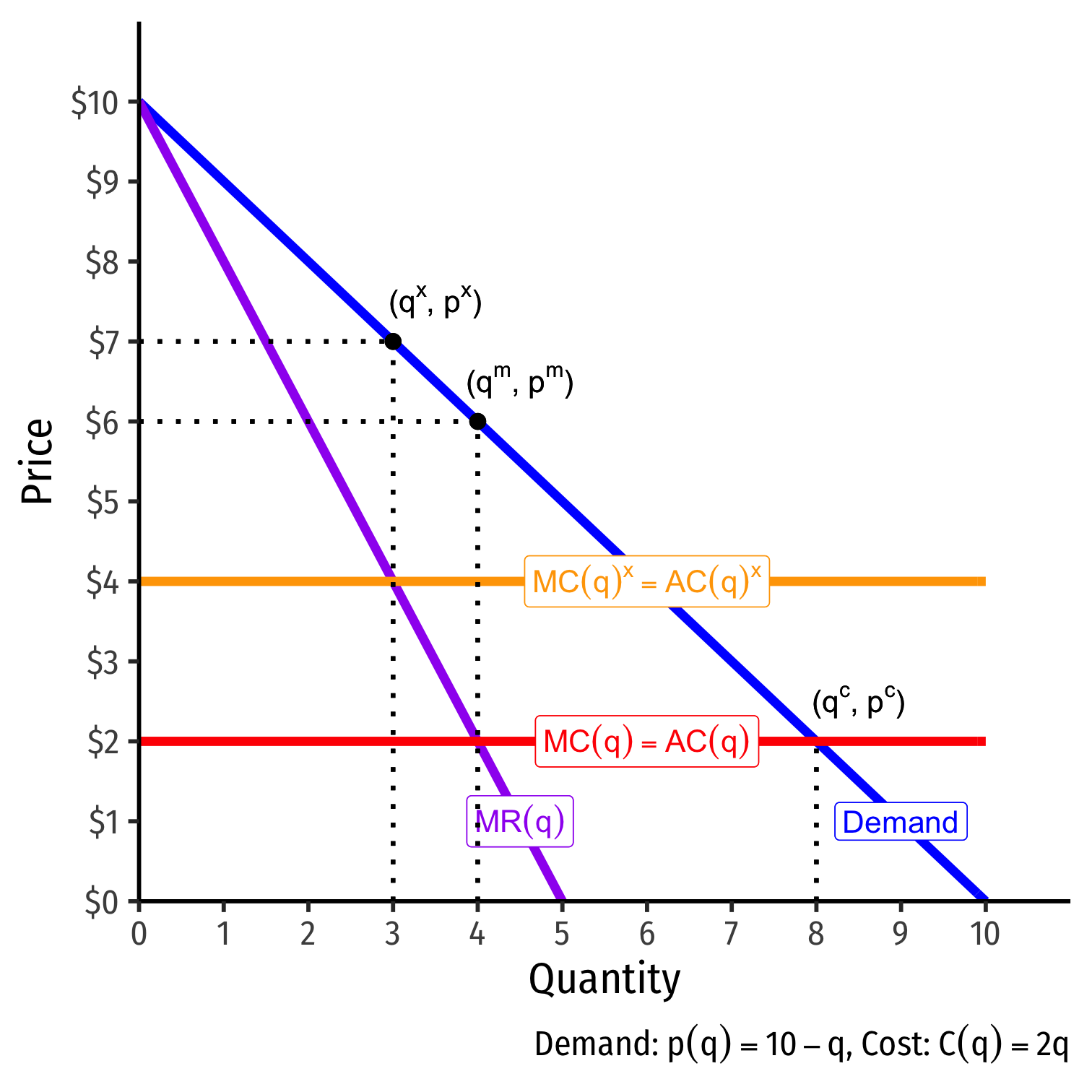
"The best of all monopoly profits is a quiet life" - Sir John Hicks
Monopoly may generate "X-inefficiency"
Lack of competition causes monopoly to be complacent or lazy
- May inefficiently raise costs of production
Creates further distortions (lost surpluses)
The Ugly of Monopoly: Rent-Seeking I
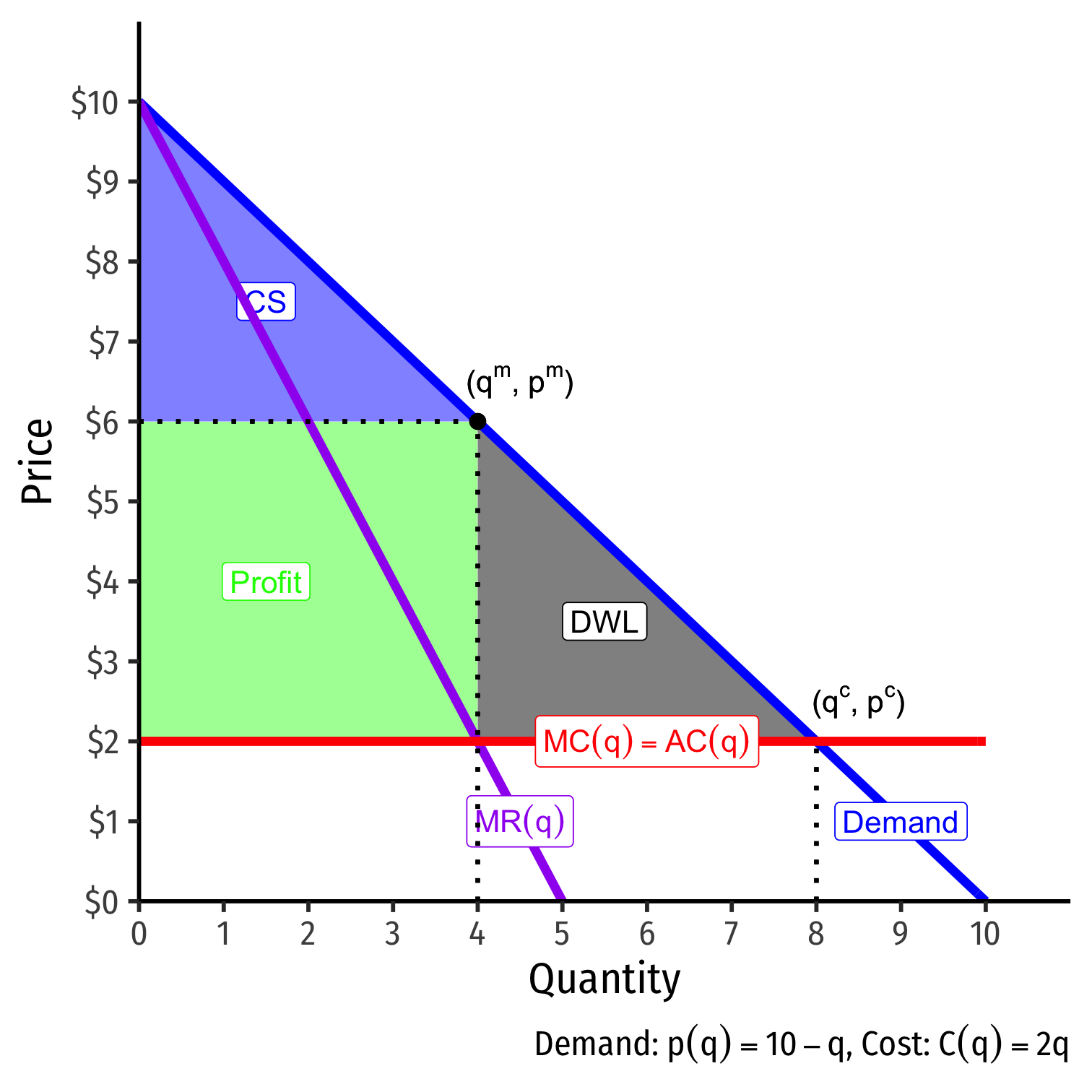
- The monopoly profits earned with market power are an economic rent
- This is the "prize" of market power
The Ugly of Monopoly: Rent-Seeking II

Think of an economic rent as a "prize," the payment a person receives for a good above its opportunity cost
Creating rents creates competition for the rents, causing people to invest resources in rent-seeking
The cost of the rent is not just the rent itself, but the resources invested in rent-seeking!
Government Intervention Creates Rents I

- Political authorities intervene in markets in various ways that benefit some groups at the expense of everyone else
- subsidies to groups (often producers)
- regulation of industries
- tariffs, quotas, and special exemptions from these
- tax breaks and loopholes
- conferring monopoly and other privileges
Government Intervention Creates Rents I

These interventions create economic rents for their beneficiaries by reducing competition
This is a transfer of wealth from consumers/taxpayers to politically-favored groups
The promise of earning a rent breeds competition over the rents (rent-seeking)
Rent-Seeking II

Gordon Tullock
1922-2014
"The rectangle to the left of the [Deadweight loss] triangle is the income transfer that a successful monopolist can extort from the customers. Surely we should expect that with a prize of this size dangling before our eyes, potential monopolists would be willing to invest large resources in the activity of monopolizing. ... Entrepreneurs should be willing to invest resources in attempts to form a monopoly until the marginal cost equals the properly discounted return," (p.231).
Tullock, Gordon, (1967), "The Welfare Cost of Tariffs, Monopolies, and Theft," Western Economic Journal 5(3): 224-232.
Antitrust
Antitrust and Competition Law I
Aren't monopolies illegal in the U.S.?
Yes: engaging in anticompetitive practices in the U.S. is illegal under antitrust laws
- Laws intended to promote economic competition and reduce excessive market power
- enforced by DOJ (criminal) and FTC (civil)


Antitrust and Competition Law II
Aren't monopolies illegal in the U.S.?
No: most monopolies exist because of explicit or implicit government-backing
- Some markets actually work better as a monopoly ("the good", natural monopoly, patents, etc.)
- Some markets and regulators are captured via rent-seeking firms to block competition ("the ugly")

Antitrust and Competition Law III

Sherman Antitrust Act (1890)
§ 1: "Every contract, combination in the form of trust or otherwise, or conspiracy, in restraint of trade or commerce among the several States, or with foreign nations, is declared to be illegal."
§ 2: "Every person who shall monopolize, or attempt to monopolize, or combine or conspire with any other person or persons, to monopolize any part of the trade or commerce among the several States, or with foreign nations, shall be deemed guilty of a felony [...]"
26 Stat. 209, 15 U.S.C. (\S) 1–7
Antitrust and Competition Law IV

Source: WSJ (Jan 23, 2017)
- Mergers, acquisitions, and major corporate activities are scrutinized by DOJ and FTC on antitrust grounds
Sources of Market Power
Control Over a Key Resource
Control Over a Key Resource I


Being one of the largest providers of a resource where there are few substitutes
Aluminum Company of America (Alcoa) once controlled 90% of the market for bauxite (used to create aluminum), and produced 63% of world aluminum supply
United States v. Alcoa 148 F.2d 416 (2d Cir. 1945)
Control Over a Key Resource II


- De Beers once owned 85% of the world's diamond supply
Control Over a Key Resource: Inventors?

What about inventors and new products?
Every first producer enjoys monopoly power...for a time
Eventually, new entrepreneurs find a way to compete and enter the market with substitutes
Control Over a Key Resource: Inventors?

What about inventors and new products?
Every first producer enjoys monopoly power...for a time
Eventually, new entrepreneurs find a way to compete and enter the market with substitutes
Control Over a Key Resource: Inventors?

What about inventors and new products?
Every first producer enjoys monopoly power...for a time
Eventually, new entrepreneurs find a way to compete and enter the market with substitutes
Control Over a Key Resource: Inventors?

What about inventors and new products?
Every first producer enjoys monopoly power...for a time
Eventually, new entrepreneurs find a way to compete and enter the market with substitutes
UNLESS...
Barriers to Entry
Barriers to Entry
- Barrier to entry: something that makes it costly, difficult, or even illegal for competitors to enter a market & compete with incumbent firm(s)
- technological advantage
- name recognition
- high fixed/sunk costs
- intellectual property rights
- occupational licensing
- government granted privileges
- regulatory compliance

Barriers to Entry: Legal Prohibitions

The United States Postal Service is the only provider of first class mail allowed by order of the government
Starting another business that delivers mail is illegal
Note: FedEx and UPS deliver express packages, can not deliver mail or use USPS mailboxes
Barriers to Entry: Taxis I


Barriers to Entry: Taxis II

Barriers to Entry: Taxis III


If You Look at the World Long Enough...

Regulation has a Dark Side

George Stigler
1911-1991
Economics Nobel 1982
"[A]s a rule, regulation is acquired by the industry and is designed and operated primarily for its benefits," (p.3).
Stigler, George J, (1971), "The Theory of Economic Regulation," Bell Journal of Economics and Management Science 3:3-21
Barriers to Entry: Occupational Licensing I

In 1950, 1 in 20 jobs required a license. Today it's 1 in 4. Source: Obama White House (2015): Occupational Licensing: A Framework for Policymakers
Barriers to Entry: Occupational Licensing II
Barriers to Entry: Occupational Licensing III

Barriers to Entry: Occupational Licensing IV

"'It is illegal in the state of Utah to do any form of extensions without a valid cosmetology license," the e-mail read. "Please delete your ad, or you will be reported.'
To get a license, Jestina would have to spend more than a year in cosmetology school. Tuition would cost $16,000 dollars or more."
Source: NPR Planet Money
Barriers to Entry: Intellectual Property I


Barriers to Entry: Intellectual Property II

Barriers to Entry: Intellectual Property III
For these economic reasons, patent (for ideas and inventions) and copyright (for expressions) laws exist
Grant temporary monopoly to holder in order to recover their fixed costs and provide incentive to undertake (risky and expensive) research/creativity
A utilitarian tradeoff between incentives and access


Barriers to Entry: Intellectual Property V

Economies of Scale and Natural Monopoly
Economies of Scale and Natural Monopoly I
Recall: economies of scale: as ↑q, ↓AC(q)
Minimum Efficient Scale (MES): q with the lowest AC(q)
Economies of Scale and Natural Monopoly I
Recall: economies of scale: as ↑q, ↓AC(q)
Minimum Efficient Scale (MES): q with the lowest AC(q)
If MES is small relative to market demand...
- AC hits Market demand during diseconomies of scale...
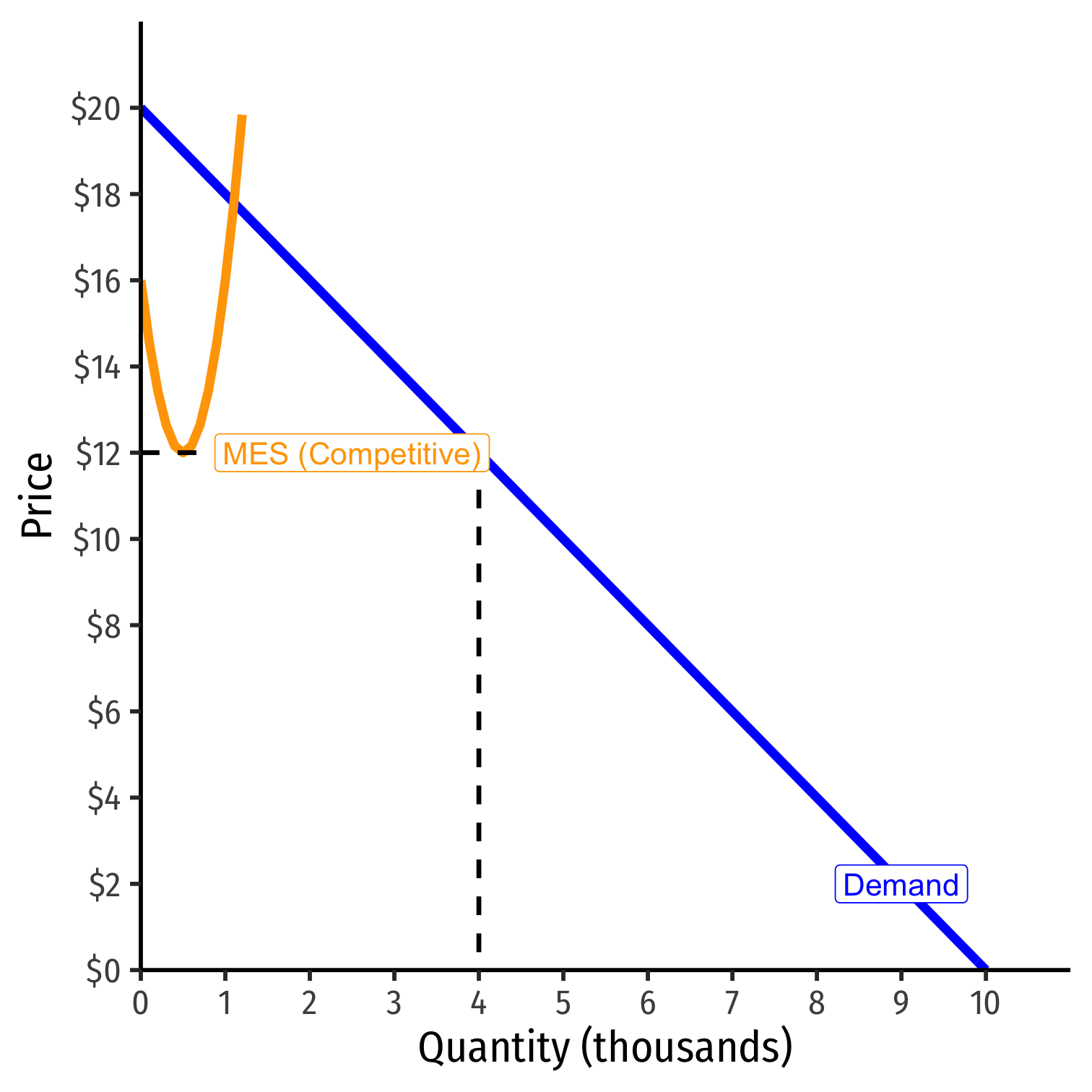
Economies of Scale and Natural Monopoly I
Recall: economies of scale: as ↑q, ↓AC(q)
Minimum Efficient Scale (MES): q with the lowest AC(q)
If MES is small relative to market demand...
- AC hits Market demand during diseconomies of scale...
- ...can fit more identical firms into the industry!
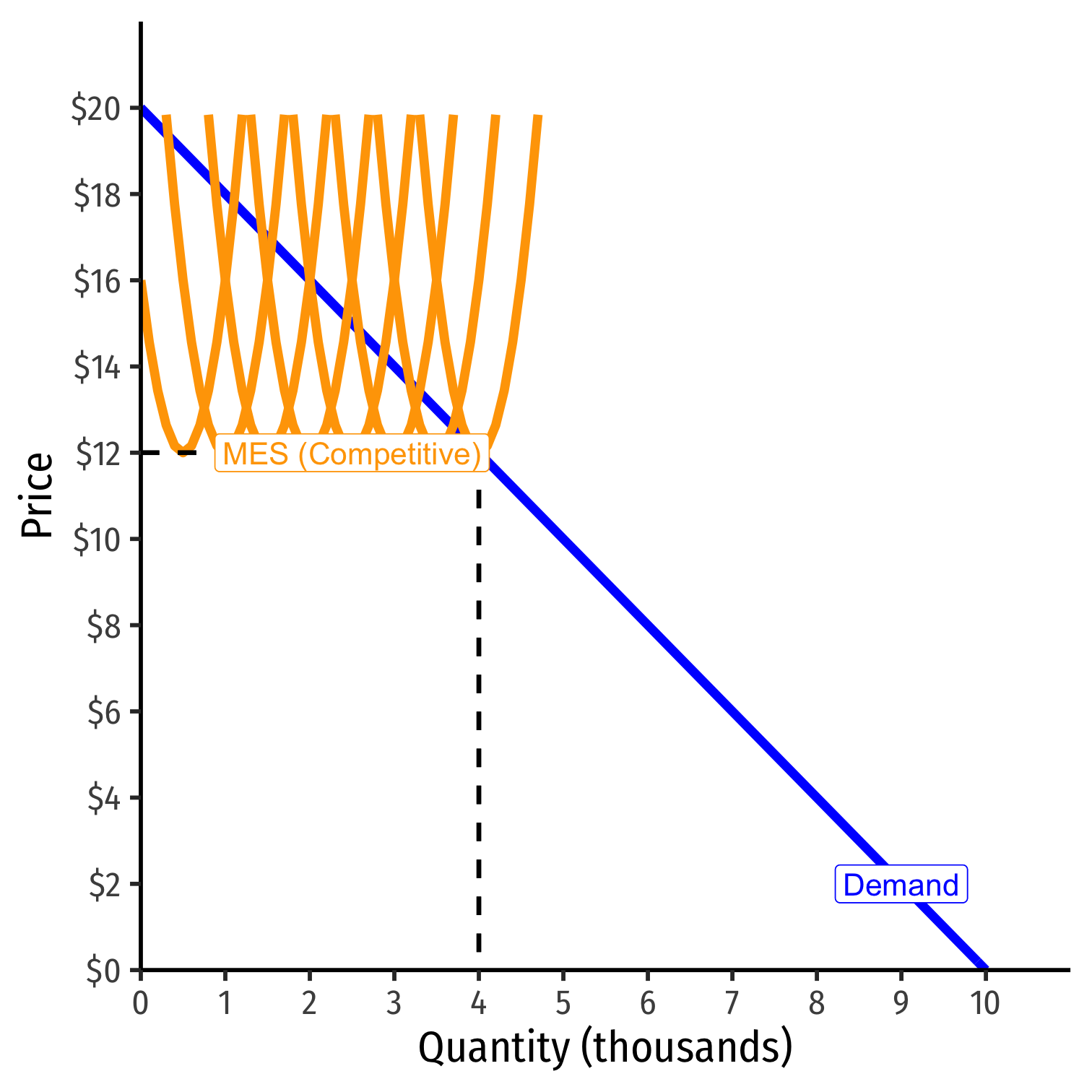
Economies of Scale and Natural Monopoly I
- If MES is large relative to market demand...
- AC hits Market demand during economies of scale...
- likely to be a single firm in the industry!
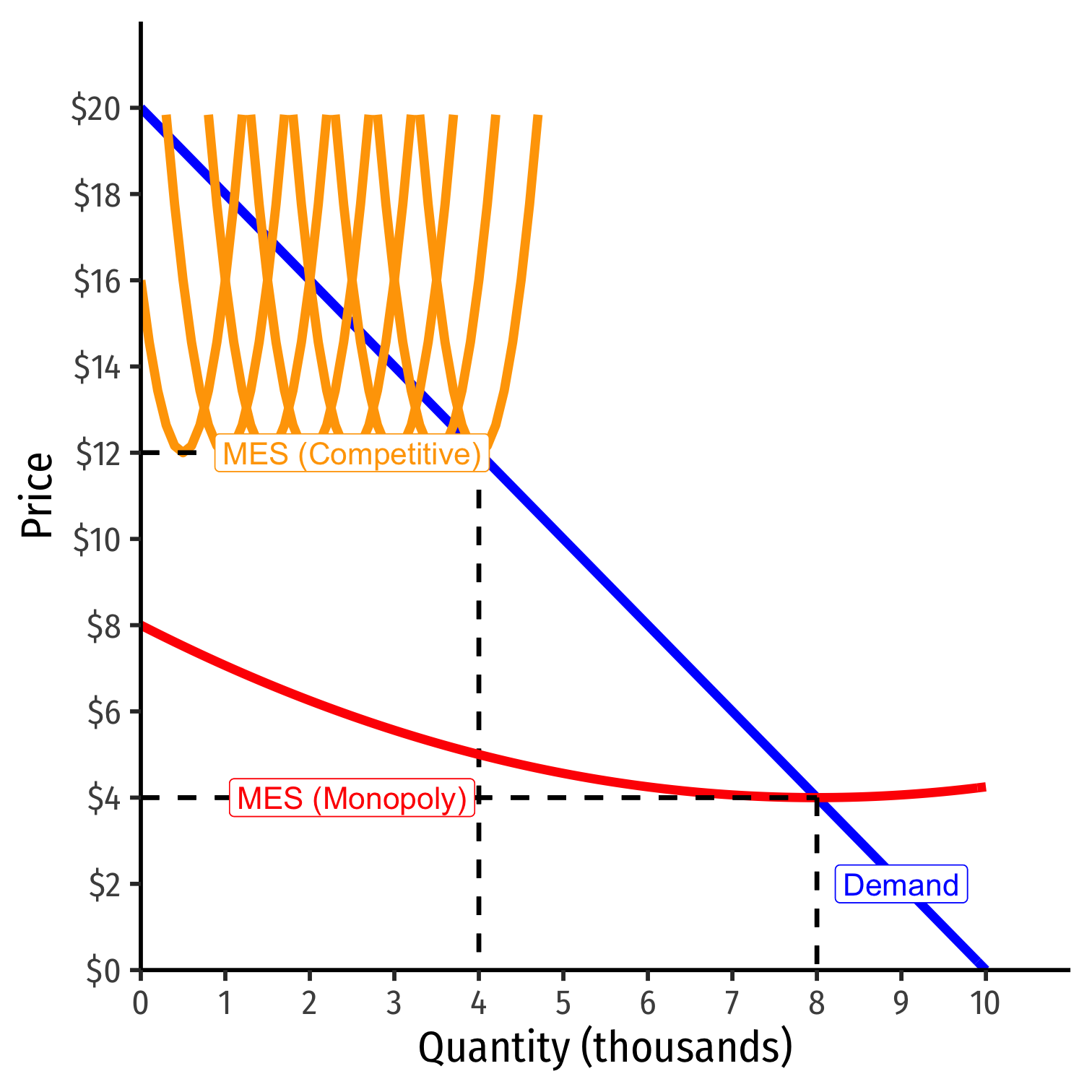
Economies of Scale and Natural Monopoly I
If MES is large relative to market demand...
- AC hits Market demand during economies of scale...
- likely to be a single firm in the industry!
A natural monopoly that can produce higher q∗ and lower p∗ than a competitive industry!
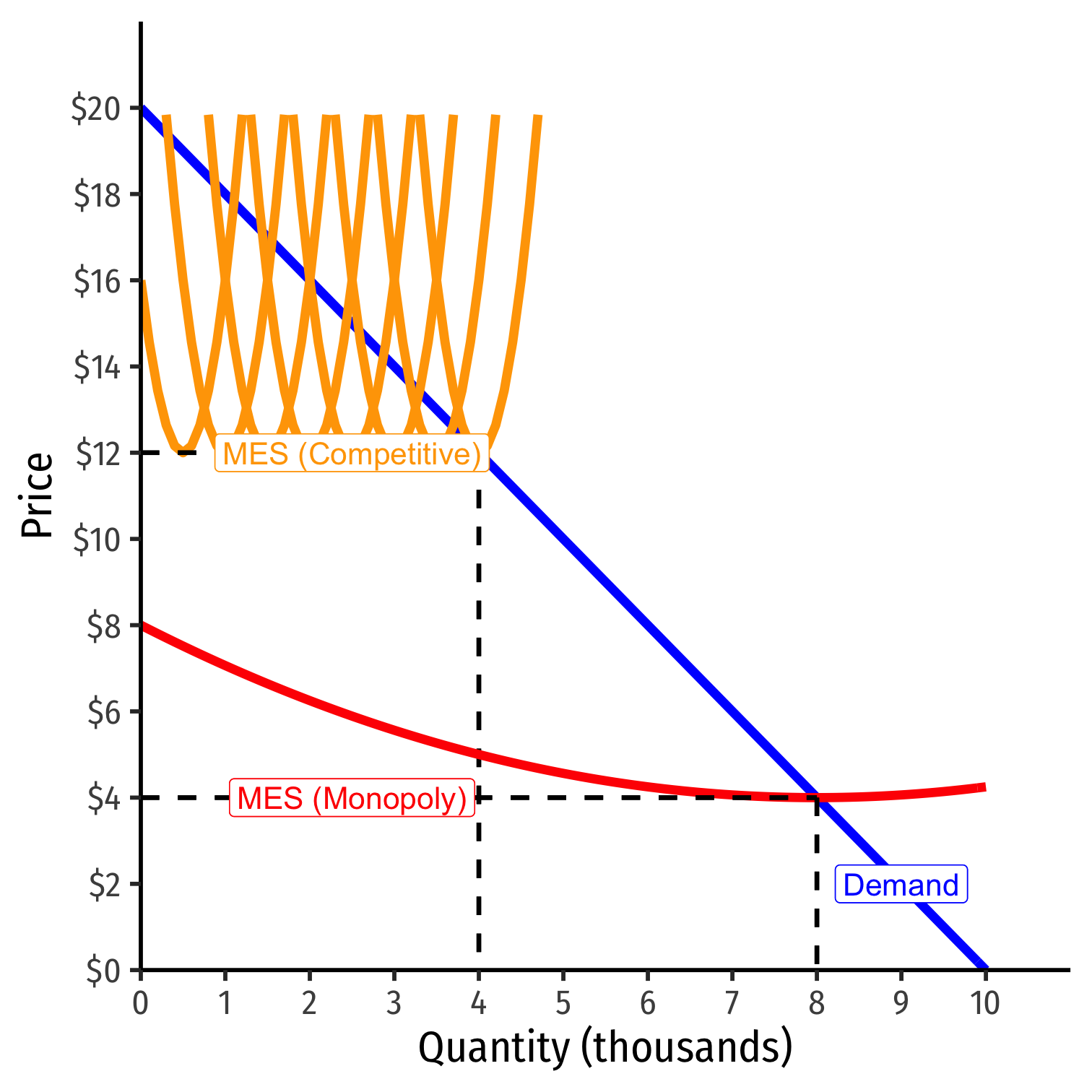
Economies of Scale and Natural Monopoly II
Example: Imagine a single isolated condo complex with 1,000 units far from any other buildings or telco infrastructure
- Fixed costs: laying cable to the complex is $100,000
- Marginal costs: connecting each unit: $0

Economies of Scale and Natural Monopoly II
- Suppose 10 providers serve the complex, each laying down their own cables, and each serving 100 units:
Average cost=$100,00010=$1,000 per subscriber

Economies of Scale and Natural Monopoly II
- Suppose 1 provider serves the complex serving all 1,000 units:
Average cost=$100,0001000=$100 per subscriber

Regulating Natural Monopolies
Governments avoid "wasteful duplication" of competition, grant exclusive franchises, a single monopolist allowed in geographic region
Provider made a common carrier: monopolist must provide universal service to all
Rate of return regulation: gov't and monopolist agree on a price to guarantee a "modest return on capital" (i.e. some π>0)
- Attempting to ↑q and ↓p
- Prohibition on price discrimination, enforced subsidies

Regulating Natural Monopolies II
Locations with only 1 (wireline) broadband provider Source: FCC: Broadband Provider Map




